When you think about electrical wiring, the materials used for the wires themselves may not always come to mind. Yet, understanding these materials, especially copper-clad wire, can significantly impact your projects and ensure you’re making the right choices for efficiency, cost, and performance. So, what exactly is copper-clad wire, and why is it such a vital part of modern electrical and electronic systems? In this article, I’ll walk you through everything you need to know about copper-clad wire, from its composition to its uses and advantages.
I’m sure you’ve come across this material in various applications, but by the end of this guide, you’ll have a deep understanding of why copper-clad wire is a game-changer in the world of electrical engineering and manufacturing.
Understanding Copper Clad Wire
At its core, copper-clad wire is a type of wire that has a layer of copper bonded to a substrate metal, typically steel. This type of wire is a cost-effective solution that combines the strength and flexibility of steel with the excellent conductivity of copper.
You may also like this What Plate to Get for a Gaming Keyboard?
Composition of Copper Clad Wire
Copper-clad wire is made by cladding a thin layer of copper over a steel or other metal core. The manufacturing process can be accomplished by several methods, such as extrusion or electroplating, resulting in a wire that has copper on the outer layer while still maintaining the core’s integrity.
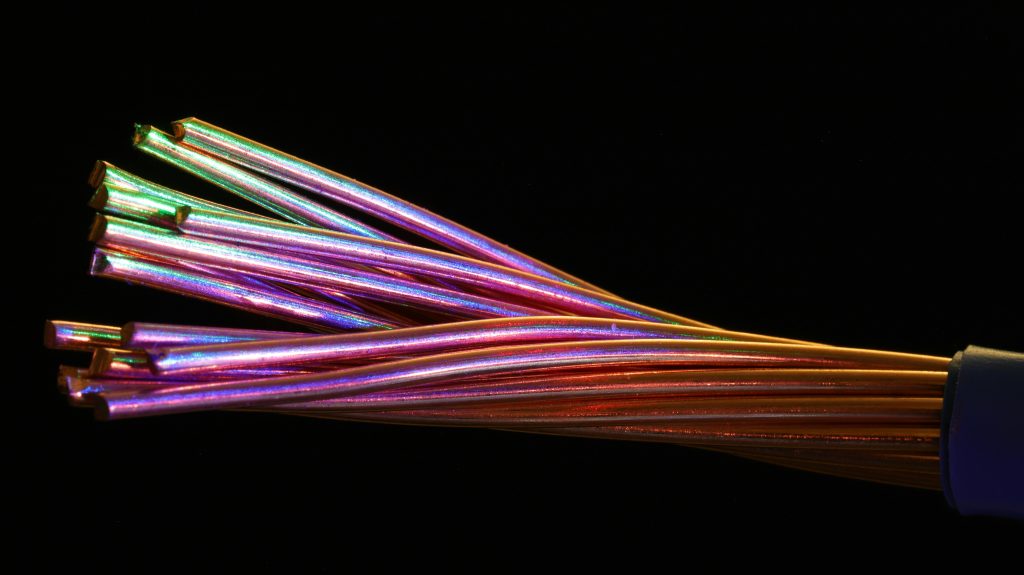

- Outer Layer: Copper – Known for its superior electrical conductivity, copper makes up the outer layer of the wire. This ensures that copper-clad wire can efficiently conduct electricity.
- Core Layer: Steel or other materials – The core provides the wire with strength and durability, making it much more flexible and less prone to breakage under tension compared to pure copper wires.
Why is Copper Clad Wire Important?
Copper-clad wire provides a range of benefits that make it an attractive option for various applications. By understanding its importance, you’ll appreciate how copper-clad wire helps solve challenges in electrical conductivity and structural integrity.
Superior Conductivity at a Lower Cost
One of the key selling points of copper-clad wire is its excellent electrical conductivity, which is a hallmark of copper. However, using pure copper can be expensive, especially in large-scale applications. By cladding the copper onto a steel core, manufacturers can offer the conductivity benefits of copper at a much more affordable price point. This makes it an ideal option for industries where high-quality conductivity is necessary but budget constraints exist.
Improved Mechanical Properties
The steel core in copper-clad wire significantly improves its mechanical properties. Steel is known for its strength, so the combination of copper and steel results in a wire that is both flexible and robust. This is especially useful for applications that require wires to be bent, twisted, or pulled without losing their shape or breaking.
Applications of Copper Clad Wire
Copper-clad wire is used in a variety of industries and applications, thanks to its unique blend of conductivity, strength, and cost-effectiveness. Let’s take a closer look at some of the most common uses of copper-clad wire.
Telecommunications and Data Transmission
In telecommunications, data transmission requires the use of wires that can efficiently carry signals over long distances. Copper-clad wire is a popular choice for coaxial cables, which are used in television, internet, and telephone systems. The copper provides the signal-carrying capability, while the steel core offers added structural strength.
Electrical Wiring for Low Voltage Systems
Copper-clad wire is also widely used in electrical wiring, particularly in low voltage systems. Due to its high conductivity, copper-clad wire is an excellent choice for applications like automotive wiring, low-voltage power transmission, and even solar panel systems.
Speaker Wires and Audio Equipment
For audio equipment, the conductivity of copper-clad wire is crucial. Copper-clad wires are often used as speaker wires because they offer both the needed flexibility and the high conductivity required to deliver clear sound quality. Additionally, these wires are relatively cost-effective compared to pure copper speaker cables.
Transformers and Inductors
Copper-clad wire plays a significant role in the manufacturing of transformers and inductors. These components rely on tightly wound coils of wire to function efficiently. The steel core of copper-clad wire provides the necessary strength to withstand the winding process, while the copper outer layer ensures optimal electrical conductivity.
Benefits of Copper Clad Wire
The use of copper-clad wire offers several advantages over other types of wire. Let’s examine the most notable benefits that make it such a preferred material for many applications.
| Feature | Copper-Clad Wire | Pure Copper Wire | Aluminum Wire | Steel Wire |
| Electrical Conductivity | High | Very High | Low | Low |
| Strength | High | Moderate | Low | Very High |
| Cost | Affordable | Expensive | Low | Affordable |
| Flexibility | Moderate | High | Moderate | Low |
| Durability | High | High | Moderate | Very High |
Cost-Effectiveness
One of the major reasons why copper-clad wire is so popular is its cost-effectiveness. By using a steel core instead of pure copper, manufacturers can reduce costs while still maintaining high conductivity. This makes it an attractive option for industries that need to minimize material costs without sacrificing performance.
Strength and Durability
The strength of copper-clad wire comes from its steel core. Steel is a durable material that provides the wire with the necessary resistance to breakage and tension. This makes copper-clad wire more durable and reliable, especially for applications that require frequent handling, bending, or exposure to stress.
Versatility
Copper-clad wire is versatile and can be used in a wide range of industries. Whether you’re wiring a telecommunications system, building an inductor, or installing electrical components in an automobile, copper-clad wire can be adapted to meet your needs. Its blend of conductivity, strength, and flexibility makes it suitable for diverse applications.
Pros and Cons of Copper Clad Wire
As with any material, there are both advantages and drawbacks to using copper-clad wire. Understanding these pros and cons will help you determine if this type of wire is suitable for your specific application.

Pros of Copper Clad Wire
- High electrical conductivity at a lower cost than pure copper wire.
- Durable and resistant to damage, thanks to the steel core.
- Flexible enough for various applications but stronger than pure copper wire.
- Affordable compared to pure copper wire or other premium options.
Cons of Copper Clad Wire
- Lower conductivity than pure copper wire, though still very good.
- Not as flexible as pure copper wire, making it less ideal for extremely tight bends.
- May corrode over time if exposed to harsh environmental conditions, especially in outdoor settings.
Choosing the Right Copper Clad Wire for Your Application
When selecting copper-clad wire for a project, you need to consider several factors. Let’s break down the key considerations to help you make the right choice.
Consider Electrical Conductivity Needs
If your application demands the highest possible electrical conductivity (e.g., high-speed data transmission), you might want to opt for pure copper wire. However, if cost is a concern and high conductivity is still sufficient for your needs, copper-clad wire is an excellent alternative.
Assess the Strength Requirements
For projects where the wire will be subjected to physical stress, copper-clad wire may be the ideal choice due to its strong steel core. However, for applications requiring maximum flexibility, you might prefer a wire made from pure copper or other materials.
Budget and Cost-Effectiveness
If you’re on a budget, copper-clad wire offers a balance between cost and performance. It provides a reliable solution at a fraction of the cost of pure copper wire, making it ideal for large-scale applications where saving on material costs is crucial.