In today’s world, where nearly every business, service, and individual relies on cloud infrastructure, the importance of understanding What is Cloud Computing Cyber Security Fundamentals cannot be overstated. Whether you’re handling sensitive data, managing virtual networks, or ensuring that your cloud applications remain secure, mastering the security aspects of cloud computing is critical.
But, as we dive into the complexities of cybersecurity in the cloud, one question remains central: How can you effectively safeguard your data in an environment that is constantly evolving?
In this article, we will explore the fundamental aspects of What is Cloud Computing Cyber Security Fundamentals. By the end, you’ll understand key concepts, security measures, and best practices to secure your cloud environment.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is the delivery of computing services—including storage, processing power, and databases—over the internet, or “the cloud.” These services are hosted and maintained by cloud providers, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud. The beauty of cloud computing lies in its flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness.
The Relationship Between Cloud Computing and Cybersecurity
As businesses increasingly migrate to the cloud, the importance of securing data stored in the cloud is paramount. Cloud computing offers numerous benefits, including remote access, cost-efficiency, and seamless collaboration, but it also introduces new What is Cloud Computing Cyber Security Fundamentals risks.
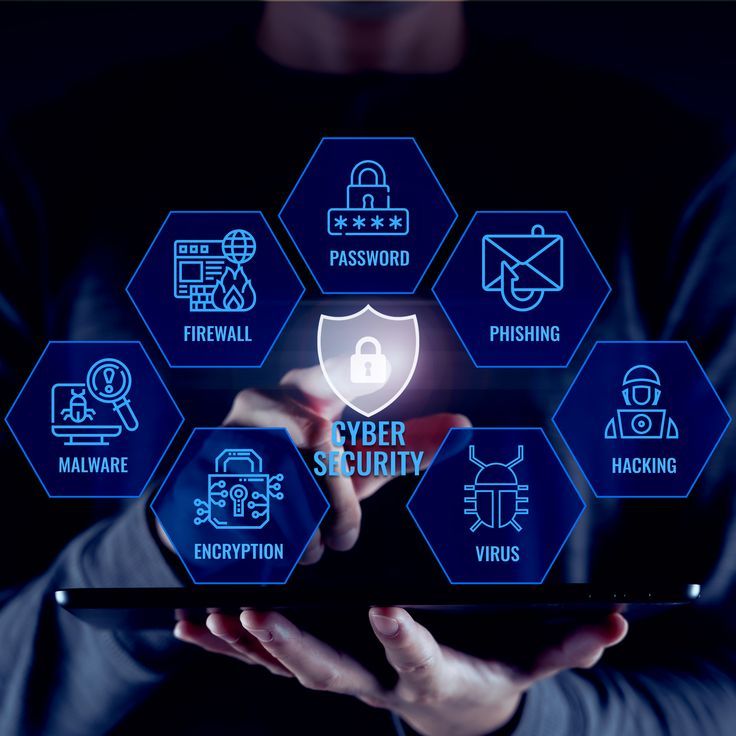
Cybersecurity in the cloud involves protecting data, applications, and services from unauthorized access, breaches, and attacks. With cyberattacks becoming more sophisticated, cloud security plays a pivotal role in maintaining the integrity and privacy of digital assets.
Why is Cloud Security Important?
Cloud security is critical because cloud environments are often targeted by cybercriminals due to the vast amounts of sensitive data they store. Here’s why cloud security is essential for businesses:
- Data Protection: Protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access and ensuring data privacy.
- Compliance Requirements: Adhering to industry regulations and compliance standards.
- Operational Continuity: Maintaining business operations even in the event of a cyber attack.
Key Principles of Cloud Computing Cybersecurity
To understand cloud computing security fundamentals, let’s break down the primary principles that make up a strong cloud security strategy:
1. Data Encryption
Data encryption is one of the core principles in cloud security. It ensures that data is unreadable without the appropriate decryption key. Whether data is at rest, in transit, or during processing, encryption acts as a safeguard against unauthorized access. Without proper encryption, sensitive data, such as financial or personal information, can be exposed during a breach.
2. Identity and Access Management (IAM)
IAM allows organizations to manage who can access specific resources in the cloud. With IAM policies, administrators can control permissions based on user roles, ensuring that only authorized individuals have access to critical systems and data. Strong IAM includes multi-factor authentication (MFA), role-based access control (RBAC), and regular audits to verify compliance.
3. Network Security
Cloud network security is another fundamental aspect of securing cloud environments. It includes protecting the data that travels across the cloud network, securing the communication channels between cloud services, and preventing malicious traffic. Virtual private networks (VPNs), firewalls, and intrusion detection systems (IDS) are commonly used to ensure a secure network architecture.
4. Governance and Compliance
Cloud computing must also adhere to legal and regulatory frameworks, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) or Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). Organizations need to enforce governance policies to comply with these laws and protect their data and applications from regulatory violations.
Cloud Security Models: Understanding What is Cloud Computing Cyber Security Fundamentals
Cloud security doesn’t fall solely on the cloud provider—it’s a shared responsibility between the cloud provider and the client. The security responsibilities can be categorized as follows:
Cloud Service Provider’s Role:
- Securing the cloud infrastructure.
- Ensuring physical security and network protection.
- Managing the underlying hardware and platform software.
Client’s Role:
- Configuring and managing their cloud resources securely.
- Implementing IAM policies and data encryption.
- Regularly monitoring for security breaches and vulnerabilities.
Common Cloud Security Threats
To effectively secure your cloud infrastructure, you need to be aware of the common threats that pose risks to your data and applications. Let’s explore the most prominent threats:
1. Data Breaches
Data breaches occur when unauthorized individuals access and steal sensitive data. This can happen due to weak authentication, misconfigured cloud settings, or vulnerable applications. A single breach can compromise your organization’s reputation and result in heavy financial penalties.
2. Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks
DoS attacks aim to disrupt the availability of services by overwhelming them with a flood of malicious traffic. This can cause cloud applications to become unavailable, impacting the operations of businesses that rely on cloud infrastructure.
3. Insider Threats
Not all threats come from external sources. Insider threats, from employees or contractors with malicious intent, can compromise cloud systems and data. Preventing insider threats requires continuous monitoring, role-based access, and training for staff on security best practices.
4. Account Hijacking
Account hijacking involves attackers stealing login credentials to gain unauthorized access to cloud-based applications or services. This type of attack can result in unauthorized financial transactions, data manipulation, or identity theft.
Cloud Security Best Practices
To mitigate the risks associated with What is Cloud Computing Cyber Security Fundamentals, organizations should implement these best practices:
1. Use Strong Authentication Mechanisms
Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) and strong password policies for all users accessing cloud services. MFA adds an additional layer of security, making it harder for attackers to compromise accounts.
2. Conduct Regular Security Audits
Conduct periodic audits to ensure that your cloud infrastructure remains secure. Regularly evaluate your system configurations, access controls, and encryption settings to identify and address vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
3. Implement Data Backups and Recovery Plans
Ensure that your cloud data is regularly backed up and that you have a disaster recovery plan in place. This minimizes data loss in the event of a cyberattack or system failure, helping you maintain business continuity.
4. Monitor Cloud Resources Continuously
Regularly monitor your cloud environment for suspicious activity. Intrusion detection and real-time monitoring can help detect anomalies and prevent potential breaches.
5. Use Cloud Security Solutions
Many cloud providers offer security tools and solutions, such as firewalls, encryption services, and monitoring tools. Take advantage of these built-in security features to enhance your cloud security posture.
Comparison Table: Cloud Security Features
| Feature 1 | Feature 2 | Feature 3 | Feature 4 |
| Data Encryption | Multi-Factor Authentication | Identity Management | Vulnerability Scanning |
| Protects data at rest, transit, and processing | Adds layers of security beyond passwords | Ensures only authorized access | Helps identify weak points in the system |
| Essential for sensitive data | Crucial for user account safety | Prevents unauthorized data access | Minimizes risks by detecting vulnerabilities |
Pros and Cons of What is Cloud Computing Cyber Security Fundamentals Security
Pros:
- Scalability: Cloud services can scale security measures to accommodate increasing data volumes.
- Centralized Security Management: Security tools and policies can be implemented and managed from a central dashboard.
- Cost Efficiency: Cloud providers invest in robust security measures, saving businesses the cost of building their own security infrastructure.
Cons:
- Complexity: Configuring and managing security for cloud environments can be complex, especially for large organizations.
- Dependence on Providers: Businesses rely on cloud providers for infrastructure security, which can create gaps in security if providers fail to implement proper protections.
- Shared Responsibility Model: Both cloud providers and clients share security duties, which may lead to confusion or gaps in responsibility.
Tech Specs: Cloud Security Tools
- Encryption Algorithms: AES-256, RSA-2048
- IAM Solutions: AWS IAM, Microsoft Azure AD
- Firewalls: Palo Alto Networks, Cisco ASA
- Monitoring Tools: CloudWatch (AWS), Azure Security Center
- Backup Services: AWS Backup, Google Cloud Backup
Recommendations for Effective Cloud Security
- Choose a trusted cloud provider with robust security features and compliance certifications.
- Implement strong access control policies to limit data access.
- Regularly test your cloud security with penetration testing and vulnerability assessments.
Stay updated on new cloud security threats and adjust your defenses accordingly. you may like this. Is HVLIION Karno Engine New Technology OV?